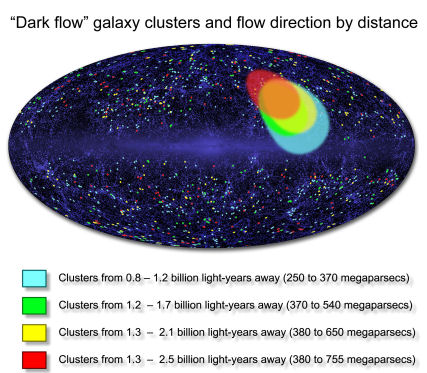
Led by Alexander Kashlinsky at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, a new study of distant galaxy clusters mysteriously streaming at a million miles per hour towards the constellations Centaurus and Hydra has tracked this enigmatic “dark flow” to twice the distance originally reported. “This is not something we set out to find, but we cannot make it go away,” Kashlinsky said. “Now we see that it persists to much greater distances – as far as 2.5 billion light-years away.”
Reporting the findings in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, Kashlinksy notes that the clusters appear to be moving along a line extending from our solar system toward Centaurus/Hydra, but the direction of this motion is less certain. Evidence indicates that the clusters are headed outward along this path, away from Earth, but the team cannot yet rule out the opposite flow. “We detect motion along this axis, but right now our data cannot state as strongly as we’d like whether the clusters are coming or going,” he added.
The dark flow is controversial in astronomy circles because the distribution of matter in the observed universe cannot account for it. Its existence suggests that some structure beyond the visible universe is pulling on matter in our vicinity. This shouldn’t be happening as large-scale motion in the universe should show no preferred direction.
To isolate the anomaly, Kashlinksy focused on the way in which the hot X-ray-emitting gas within a galaxy cluster scatters photons from the cosmic microwave background (CMB). Because galaxy clusters don’t precisely follow the expansion of space, the wavelengths of scattered photons change in a way that reflects each cluster’s individual motion.
But in 2000, Kashlinsky, working with Fernando Atrio-Barandela at the University of Salamanca, Spain, demonstrated that it was possible to tease the subtle signal out of the measurement noise by studying large numbers of clusters.
In 2008, armed with a catalog of 700 clusters assembled by Harald Ebeling at the University of Hawaii and Dale Kocevski, now at the University of California, Santa Cruz, the researchers applied the technique to the three-year WMAP data release. That’s when the mystery motion first came to light. The new study builds on the previous one by using the five-year results from WMAP (see links below) and by doubling the number of galaxy clusters.
“It takes, on average, about an hour of telescope time to measure the distance to each cluster we work with, not to mention the years required to find these systems in the first place,” Ebeling said. “This is a project requiring considerable follow-through.”
According to Atrio-Barandela, who has focused on understanding the possible errors in the team’s analysis, the new study provides much stronger evidence that the dark flow is real. He points out that the brightest clusters at X-ray wavelengths hold the greatest amount of hot gas to distort CMB photons. “When processed, these same clusters also display the strongest KSZ signature – unlikely if the dark flow were merely a statistical fluke,” he said.
The team then sorted the cluster catalog into four “slices” representing different distance ranges (pictured). They then examined the preferred flow direction for the clusters within each slice. While the size and exact position of this direction display some variation, the overall trends among the slices exhibit remarkable agreement.
The researchers are currently working to expand their cluster catalog in order to track the dark flow to about twice the current distance. Improved modeling of hot gas within the galaxy clusters will help refine the speed, axis, and direction of motion. Future plans call for testing the findings against newer data released from the WMAP project and the European Space Agency’s Planck mission, which is also currently mapping the microwave background.
Related:
New 3-D Map Of Cosmos Is Biggest Ever
Big Bang Brouhaha Brewing
Physicists Mull Big Bang Detritus
















Comments are closed.